During the past three decades replacement of missing teeth with implant supported restorations has become increasingly common. Dental implant placement is a viable option for both complete and partially edentulous cases, and is often the treatment of choice. While implant supported restorations do not share the risk of dental caries that natural teeth are subject to, they are susceptible to peri-implant mucositis and peri-implantitis, just as the natural dentition is subject to gingivitis and periodontitis. It is well established that periodic periodontal maintenance can optimize the long-term prognosis of the natural dentition.
Like-wise, successful dental implant therapy must include an appropriate recall program. This article will review the similarities and differences of the hard and soft supporting tissues of natural teeth and dental implants, discuss the etiology and pathogenesis of peri-implant mucositis and peri-implantitis, and present a protocol for a comprehensive implant maintenance program.
Periodontitis vs Peri-implantitis
The dentogingival complex associated with natural teeth consists of the gingival sulcus, the junctional epithelium, and the connective tissue attachment. The connective tissue fibers are oriented perpendicular to the long axis of the tooth and insert into the root surface cementum.1,2,3 While there is a sulcus and junctional epithelium associated with dental implants, the connective tissue fibers are oriented parallel to the long axis of the implant and the attachment is an adhesion.4,5 Whether the difference in the nature of connective tissue attachment results in greater risk of attachment loss for implants is not known. For natural teeth, animal studies have shown no difference in risk of breakdown comparing connective tissue and junctional epithelial attachments.6
The composition of the microbial flora associated with natural teeth and implants is similar.7,8 Periodontal pathogens are reduced but not totally eliminated in completely edentulous patients, leaving these patients at some risk for colonization of implant surfaces.9,10 A major etiologic factor in periodontitis is the formation of a biofilm harboring pathogenic bacteria, and this is also true for peri-implantitis. Bacterial colonization of implant abutments has been found to be similar on both zirconia and titanium abutments.11
Peri-implantitis is defined as an inflammatory process affecting the tissues around an osseointegrated implant in function, resulting in loss of supporting bone. Peri-implant mucositis is defined as reversible inflammatory changes of the peri-implant soft tissues in the absence of bone loss.12,14 The prevalence of peri-implantitis has been reported to be as low as approximately 10% to as high as 47%; the prevalence of peri-implant mucositis is generally greater, ranging from 32% to 80%.13-17
Periodontal and peri-implant bone turnover is a balanced dynamic process that involves resorption and formation, controlled and influenced by the local production of cytokines, with a wide range of inflammatory, hemopoietic, metabolic and immunomodulatory properties.18,19
Peri-implant microbial contamination or infection (bacteria and viruses) elicit an immune response regulated by key cytokines (TNF-a, Interleukin [IL]-1ß, TGF- ß, IL-10) that control the progression and/or suppression of the inflammatory response. Over-production of pro-inflammatory cytokines, released by monocytes / macrophages and T cells in response to a microbial challenge can lead to the breakdown of the periodontal or peri-implant tissues.20 It has been observed that the subgingival microbiota around implants affected by pocketing and bone loss presented high levels of periodontal pathogens and periodontally involved teeth in partially edentulous patients may serve as microbial reservoirs.21,22 In addition, surgical trauma in part is responsible of an early hyper-inflammatory response which is characterized by both TNF-α and IL-1ß release.23 On the other hand, ions released from dental implants can stimulate peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) to produce IL-1ß and TNF-a in vitro.24 Commercially pure titanium and titanium alloys also have been associated with the production of other cytokines such as IL-6 and IL-18.25
IL-1ß and TNF-a appear to play major roles in mediating the inflammatory response in the pathogenesis of many chronic inflammatory diseases, such as rheumatoid arthritis.26,27 IL-1ß is present at elevated levels in the gingival crevicular fluid (GCF) in the course of periodontitis and peri-implant inflammation.28,29 It is produced primarily by monocytes, but may be produced by other nucleated cells in response to injury.24 TNF-a, a cytokine with some functions similar to those of IL-1ß, has been detected in sites affected by periodontitis.30 Moreover, TNF-a and IL-1ß act synergistically to initiate the cascade of inflammatory mediators.31
IL-6 has pro-inflammatory effects and is responsible for collagen resorption of gingival tissues,32 while IL-10 is an inhibitor of inflammation.33 Other cytokines, such as IL-12 appear to induce the secretion of IFN-g from activated T and NK cells,34 and IL-8 acts as potent chemoattractant for neuthrophils35 in gingival tissues.
The continuous balance that exists between the host immune response and potential subgingival pathogens (bacteria / viruses) determines the clinical condition, not only around teeth, but also around osseointegrated dental implants. Nowzari et al. analyzed the production of cytokines around clinically healthy teeth and dental implants and examined their relationship to putative periodontal pathogens.36 Although no specific microbiological profile was observed, teeth allowed for more colonization by P. gingivalis, T. forsythia, Fusobacterium spp. Microscopic structural differences between dental and implant surfaces could account for this finding.
There is no information available on the detection of HCMV around healthy dental implants. In contrast to implants, HCMV has been detected in low frequencies around periodontally healthy teeth. Nowzari et al. did not detect HCMV around healthy dental implants using nested PCR. 36 The absence of prominent inflammation could help explain this result. Studies addressing a potential pathologic role of HCMV around implants are needed.
A tendency towards more cytokine production was observed around implants in contrast to teeth, but a specific explanation for this finding is not available.37 It can be implied that an implant acts as a foreign object and results in cytokine secretion. This raises the issue of an immune response against the chemical components of the implant. Perala et al.38 indicated that dental implant surfaces may lead to an activation of human peripheral blood mononuclear cells for the secretion of IL-1b and TNF-a.
Titanium particles in vitro have been shown to influence release of IL-2, TNF-a and IL-6.39 Sedarat et al.40 in an in vitro controlled experiment exposed titanium implants to an environment similar to in vivo conditions and measured 16 (± 5) ng/cm2/day dissolution of titanium and titanium alloy over a 96-day period. The dissolution of titanium / titanium alloy and the ions released by the atomic process of biodegradation can explain, at least in part, the presence of cytokines where no microbial pathogens could be detected. The other contents of commercially pure titanium implants such as carbon, iron, nitrogen, oxygen and hydrogen require further evaluations.
Patients who were positive for at least one of the 11 microorganisms tested by culture had higher levels of IL-1b, TNF-a, IL-10 and IL-8 at teeth and implant sites. Virulence factors from periodontopathic bacteria (e.g. P. gingivalis) are potent stimulants for the secretion of pro-inflammatory cytokines (IL-1b, TNF-a) and the subsequent activation of matrix metalloproteinases (MMP 2) and other collagenases from gingival fibroblasts.41 Taking into consideration that active IL-b1 and TNF-a mediate a variety of biological functions including osteoclast activation,42 leukocyte recruitment and excessive production of MMPs,43 the overproduction of these cytokines at some time point could lead to bone resorption and collagen degradation. In addition, the production of IL-8 in gingival tissues is an important mechanism of polymorphonuclear neutrophils (PMNs) recruitment and constitutes a first line of immune defense. PMNs produce IL-1b in response to bacterial challenge and act in a paracrine way preventing apoptosis and increasing the phagocytic activity of other PMNs.44 Low counts of PMNs in clinically healthy gingival tissues are a common finding in histological analysis at teeth and implant sites.45 The balance between this innate response and the bacterial challenge is partly responsible for maintaining the health of gingival tissues. Nevertheless, although previous studies have reported that cytokine activity seems to be relevant for alveolar bone resorption and destruction of collagen,46,47 periodontal research to date has not yet established any particular cytokine profile that could be of predictive value for disease progression. Moreover, there is no known cytokine level threshold that could differentiate between a stable site and the initiation of a pathologic process in periodontal and peri-implant tissues.
Characteristics of healthy, stable dental implants
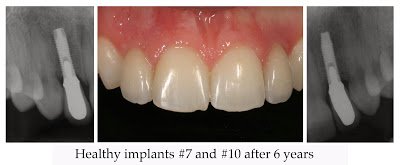
Clinical findings seen in healthy dental implants include firm pink peri-implant mucosa, shallow probing depths (≤ 3 mm), absence of bleeding upon gentle probing, absence of purulence or suppuration, and non-responsive to percussion.48 Implant supported restorations should provide comfortable function and appropriate esthetics. Radiographic bone levels are generally located at the first thread of the implant fixture.49
It is important, however, to keep in mind that standard dental radiographs are two-dimensional and do not generally provide information regarding buccal, lingual or palatal bone levels. Assessment of buccal, lingual and palatal attachment levels is accomplished by gentle probing.
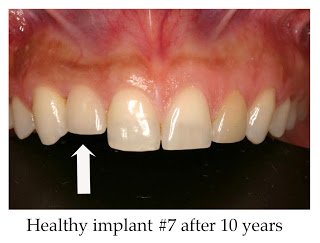
Clinical findings seen in healthy dental implants include firm pink peri-implant mucosa, shallow probing depths (≤ 3 mm), absence of bleeding upon gentle probing, absence of purulence or suppuration, and non-responsive to percussion.48 Implant supported restorations should provide comfortable function and appropriate esthetics. Radiographic bone levels are generally located at the first thread of the implant fixture.49
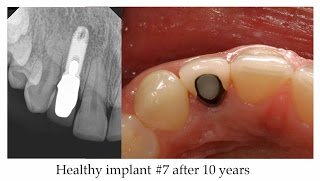
It is important, however, to keep in mind that standard dental radiographs are two-dimensional and do not generally provide information regarding buccal, lingual or palatal bone levels. Assessment of buccal, lingual and palatal attachment levels is accomplished by gentle probing.
Dental implant maintenance program
Many principles and features of maintenance therapy apply to both the natural dentition and to dental implants. In patients who are partially edentulous with implant supported restorations, maintenance visits combine traditional periodontal maintenance for the remaining natural teeth, and dental implant maintenance. In fully edentulous patients with implant supported restorations, the focus is on prevention or treatment of peri-implant mucositis or peri-implantitis, since dental caries and endodontic pathology are not possible.
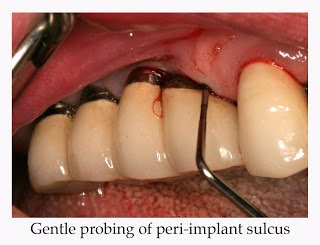
Data collection includes measurement of probing depths, bleeding upon probing, suppuration, recession, mobility, response to percussion and clinical appearance of peri-implant mucosa. Probing should be done with very gentle force, not to exceed 0.15 N; excessive force may disrupt the soft tissue attachment and has been shown to overestimate probing depths and the incidence of bleeding upon probing.50,51 As with natural teeth, inflammation of peri-implant soft tissue results in greater apical penetration of the periodontal probe.52 Hence, gentle probing has been shown to be an effective means to evaluate stability of the peri-implant attachment and to detect the presence of peri-implantitis. Follow-up periapical radiographs are generally taken one year after loading; thereafter the frequency of radiographic evaluation is determined by clinical findings.53 Care should be taken to orient the film or digital sensor parallel to the long axis of the implant fixture – this can require special attention when an angled abutment has been used for the restoration. The appearance of any pain, edema or suppuration would generally indicate the need for radiographic evaluation; otherwise, routine radiographs may be indicated only every few years.
Following examination and data collection, peri-implant conditions are documented. Then, instrumentation is performed to reduce or eliminate bacterial plaque and calcified deposits.
Standard metal scalers and curettes are not recommended for implant debridement due to the possibility of scratching the titanium surface.
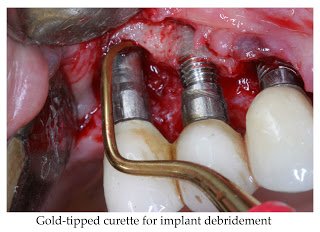
While plastic scalers are available, their effectiveness in removing hard deposits is limited; gold, titanium or vitreous carbon tipped instruments are generally more effective. Ultrasonic or piezoelectric scalers with plastic or carbon tips have also been shown to be effective without damaging implant surfaces.54,55,56
Air polishing devices and rotary rubber cups can be used for plaque removal and smoothing of implant collars.57 Biofilm disruption in the peri-implant sulcus can be accomplished with air polishing devices using either sodium bicarbonate or amino-acid glycine salt powders.58
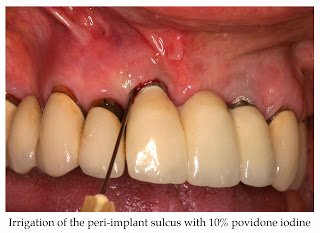
In addition to mechanical debridement using scalers and polishing devices, adjunctive local antimicrobial therapy can be administered, although limited and often equivocal evidence of enhanced clinical outcomes has been published.59-64 Irrigation of the peri-implant sulcus with the antiseptic 10% povidone iodine shown in adjacent figure.
Frequency of maintenance appointments
While it is generally agreed that periodic maintenance therapy is essential for long-term success of dental implants, the optimum frequency of recall visits is largely intuitive.49,51 Recall intervals should be individually determined for each patient, generally every three to six months. Factors to be considered in determining the frequency of maintenance visits include history of periodontitis and/or peri-implantitis, effectiveness of daily plaque control, tobacco use, rate of calculus formation, peri-implant bleeding upon probing and/or suppuration, and peri-implant probing depths.65-75
Indications for surgical intervention
While incipient peri-implantitis can often be managed successfully with non-surgical debridement, more advanced attachment loss with deeper probing depths may require surgical therapy. Indications for surgical intervention include persistent bleeding upon probing or suppuration following non-surgical therapy, radiographic evidence of progressive bone loss or persistent symptoms.76,77
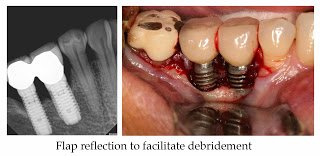
Flap reflection can facilitate granulation tissue removal and debridement of the implant surface. Mechanical debridement with plastic, carbon, gold or titanium tipped curettes, as well as with Er:YAG lasers have been used with no clear superiority of any method. Air polishing has also been advocated for debridement during peri-implant surgery, although the possibility of an air embolus should be considered. Regenerative therapy has been advocated to restore lost osseous support; however, predictable positive outcomes have not been well documented.78-83
Patient Performed Implant Hygiene Procedures
Bacterial plaque formation occurs on implant supported restorations, and, depending upon soft tissue recession and peri-implant sulcus depth, may also accumulate on abutments and implant fixtures. Plaque formation tends to be greater on rougher surfaces and in patients who smoke, although smoking may not adversely affect the long-term survival of dental implants.84-88 Just as treatment of gingivitis decreases the risk of developing periodontitis, early intervention when peri-implant mucosisits is detected reduces the risk of subsequent peri-implantitis.89-91 While dental implants may accumulate lesser quantities of bacterial plaque than natural teeth, effective daily plaque control is none-the-less essential to maintain health and stability of both hard and soft implant supporting tissues.92,93
Home care for dental implant supported restorations is generally similar to traditional oral hygiene procedures with some minor modifications. Plaque control for single implants can be accomplished with a toothbrush and dental floss; numerous studies have suggested that powered tooth brushes may be more effective than manual brushes.94-96 For implant supported fixed partial or complete dentures, floss threaders or interdental brushes are effective in controlling interproximal plaque accumulation.97-99 Interdental brushes with a teflon coated wire are preferred to minimize potential scratching. As with natural teeth, brushing and flossing are effective in disrupting supragingival plaque, with limited benefit in subgingival areas. Oral irrigation devices, particularly those with tips designed to penetrate the sulcus, have been shown to reduce bacterial levels in periodontal pockets and have been advocated as part of patients’ armamentarium for home care of dental implants. Irrigants such as plane water, saline, sea salt solution, chlorhexidine gluconate, and dilute (0.1%) sodium hypochlorite have been suggested by various authors. Based on evidence from periodontitis reports, dilute sodium hypochlorite may be the most effective antimicrobial irrigant for home use, although some patients may object to the odor or taste .100-103 For patients with remaining natural teeth a fluoride containing dentifrice is strongly recommended.
strongly recommended.
Summary
As replacement of missing teeth with implant supported restorations has become more common, increasing numbers of patients require dental implant maintenance as part of their preventive or periodontal maintenance care. While dental implants are immune to dental caries, peri-implant mucositis and peri-implantitis can occur, just as gingivitis and periodontitis is seen with the natural dentition. While there are many similarities in etiology, pathogenesis, diagnosis, maintenance therapy and the need for surgical intervention, there are some modifications in instrumentation and home care for patients with implant supported restorations. It is important when initially discussing the option of dental implant treatment that it is understood that while implants have many advantages, they do not absolve the patient from the responsibility of daily oral hygiene procedures or regular recall appointments.